Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A Complete Guide to Understanding and Using CBT for Mental Wellness
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is highly effective in healing mental health disorders. Mental health, just like physical health, is essential for a happy and fulfilling life. Cognitive behavioral therapy provides many skills to help individuals regain control over their thoughts and emotions. CBT can be helpful whether you are struggling with anxiety, depression, or healing from a traumatic experience.
What Is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?
The goal of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is to identify and fix a person’s negative thought patterns and behaviors. This type of psychotherapy, contrasting to traditional talk therapies, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), is centered around solutions, often brief, and emphasizes providing people with useful techniques to better handle their mental health.
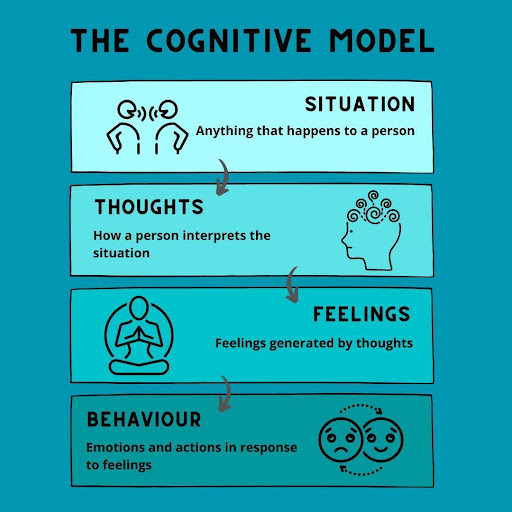
CBT’s core premise is that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. We can alter how we perceive and, ultimately, how we behave by directing irrational or harmful ideas.
History of CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy has its foundation in the 1960s, with the work of Aaron T. Beck, frequently thought to be the father of this therapeutic procedure. Beck’s analysis focused on the cognitive activities of individuals with depression, and he uncovered that twisted thinking played a crucial part in the evolution and continuation of mental healthconditions.
Since then, CBT has been the subject of large-scale research and has grown further to control a diversity of mental health disorders. By the 1990s, CBT became one of the most verification-based procedures, with countless studies supporting its success in handling anxiety, depression, PTSD, and OCD.
As of 2024, improvements in CBT testing have shown considerable adaptability of the therapy, with implementations in digital health. The rise of teletherapy programs and the success of CBT-based mobile apps have made this approach more reachable to people worldwide, providing self-help techniques shown by AI and access to professionals.
How Does CBT Work?
CBT calls for an organized treatment, generally over a set number of sessions with a certified therapist. The session typically incorporates the following steps:
1. Identifying Negative Thoughts: The first step in CBT is admitting the negative beliefs that are causing discomfort.
2. Challenging Irrational Thoughts: Once you’ve distinguished these thoughts, the therapist will guide you through procedures to confront them and question their logic.
3. Changing Behavioral Patterns: By balancing your belief patterns, CBT inspires you to embrace flourishing habits that line up with more positive thinking.
4. Practicing New Skills: CBT aligns with physical activity that you can use in daily life to control stress, anxiety, or other mental health complications.
Common CBT Techniques
Benefits of CBT for Mental Wellness
- Anxiety Disorders: CBT is usually a good option in handling generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder.
- Depression: By serving patients to point out and challenge negative beliefs, CBT has been appearing to minimize signs of depression.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Submission therapy, a part of CBT, can help individuals with PTSD procedures and control their trauma.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): CBT can help individuals handle the addictive habits and changing beliefs linked with OCD.
What to Expect from a CBT Session
- Structured Approach: Each session is goal-oriented and accompanies an organized format. You’ll start by talking about your ongoing challenges and evaluating any progress or homework from earlier sessions.
- Collaboration: CBT is a collaborative activity where you work closely with your counselor to set objectives, have an eye on improvement, and apply new skills.
- Homework Assignments: Between sessions, you’ll repeatedly be given duties or exercises to apply CBT techniques in real-life circumstances.
How Long Does treatment for CBT Take?
Unlike some other arrangements of treatment, CBT is typically short-term, with most treatment options extending from 8 to 16 sessions. Although the length of treatment may vary depending on the seriousness of the matter and how well the individual responds to therapy.
Conclusion: Rewire Your Mind for a Happier Life with CBT
By acknowledging and changing negative thought patterns for positive thinking strategies, CBT can help you rewire your mind toward inner stability. This popular technique and continuing outcomes make it a beneficial option for those looking to work on their cognitive restructuring and improve their mental well-being
FAQs:
Q1: Is CBT only for people with serious mental health conditions?
No, CBT can be a positive technique to anyone looking to handle stress, negative thought patterns, or ongoing anxiety. It is productive for both mild and extreme conditions.
Q2: Could I practice CBT techniques on my own?
Yes, many CBT techniques can be accomplished alone, but working with a trained therapist can help you to gain better results, a well trained professional is able to tailor the techniques to your particular needs.
Q3: Does CBT work for everyone?
While CBT is highly beneficial for many individuals, no therapy works for everyone. It’s crucial to find the right approach that works best for you.
Q4: Are there side effects to CBT?
CBT has very few risks. However, challenging negative thoughts and feelings can occasionally be weary for individuals. It’s crucial to work through these feelings with the help of a therapist.



